Numerical Value and Calculation as the Underlying Principle
1. Numerical Mass and General Relativity
- Numerical Mass:
- Let MM represent the numerical mass of a macroscopic object.
- This mass is associated with the curvature of spacetime, which can be described using the Einstein field equations.
- Einstein Field Equations:
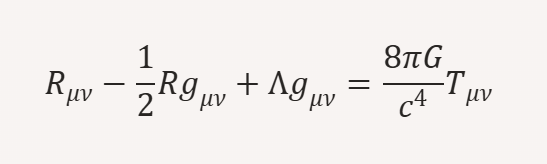
Where:
- RμνR_{\mu\nu}: Ricci curvature tensor
- RR: Scalar curvature
- gμνg_{\mu\nu}: Metric tensor
- Λ\Lambda: Cosmological constant
- GG: Gravitational constant
- cc: Speed of light
- TμνT_{\mu\nu}: Stress-energy tensor
2. Quantum State Transitions
- Quantum State:
- Let Ψ\Psi represent the quantum state of a particle.
- The evolution of the quantum state is governed by the Schrödinger equation.
- Schrödinger Equation:
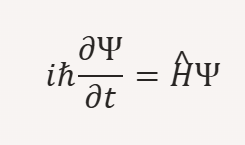
Where:
- ii: Imaginary unit
- ℏ\hbar: Reduced Planck’s constant
- H^\hat{H}: Hamiltonian operator
3. Harmonic Resonance and Numerical Sequences
- Harmonic Resonance:
- Harmonic resonance aligns quantum states with spacetime curvature.
- Let ω\omega represent the angular frequency of resonance.
4. Unified Framework: Cosmo Numerical Dynamics
- Unified Equation: Combining the principles of numerical mass, general relativity, quantum state transitions, and harmonic resonance, we derive the following unified equation:
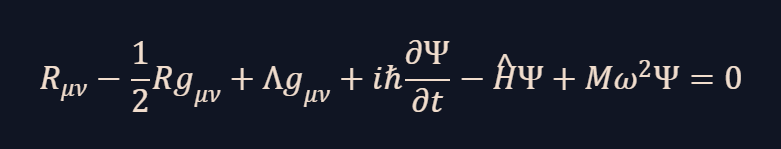
Explanation
- General Relativity Terms:
- Rμν−12Rgμν+ΛgμνR_{\mu\nu} – \frac{1}{2} R g_{\mu\nu} + \Lambda g_{\mu\nu}: Describes the curvature of spacetime caused by numerical mass.
- Quantum Theory Terms:
- iℏ∂Ψ∂t−H^Ψi \hbar \frac{\partial \Psi}{\partial t} – \hat{H} \Psi: Describes the evolution of the quantum state.
- Cosmo Numerical Dynamics Terms:
- Mω2ΨM \omega^2 \Psi: Represents the harmonic resonance between numerical mass and quantum state transitions.
This unified equation incorporates the principles of Cosmo Numerical Dynamics, general relativity, and quantum theory, providing a cohesive framework to describe both macroscopic stability and microscopic chaos. By leveraging numerical value and calculation, this equation bridges the gap between two fundamental theories in physics.
Several Theories are attempting to bridge General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics
1. Quantum Electrodynamics (QED)
- Overview: Quantum electrodynamics is a quantum field theory that describes how light and matter interact. It successfully unifies classical electrodynamics and quantum mechanics.
- Key Concept: QED explains how photons (particles of light) interact with charged particles like electrons, incorporating both wave and particle properties of light.
2. String Theory
- Overview: String theory proposes that fundamental particles are not point-like but rather one-dimensional “strings” that vibrate at different frequencies.
- Key Concept: String theory aims to unify all fundamental forces, including gravity, by describing particles as different vibrational modes of strings. It incorporates both quantum mechanics and general relativity.
3. Loop Quantum Gravity (LQG)
- Overview: Loop quantum gravity quantizes spacetime itself, proposing that spacetime has a discrete structure at the smallest scales.
- Key Concept: LQG aims to reconcile the principles of general relativity and quantum mechanics by describing gravity in a quantum framework.
4. Holographic Principle and AdS/CFT Correspondence
- Overview: The holographic principle suggests that the entire universe can be described by information encoded on a lower-dimensional boundary, like a hologram.
- Key Concept: The AdS/CFT correspondence extends this idea, proposing a duality between a gravitational theory in anti-de Sitter (AdS) space and a conformal field theory (CFT) on its boundary. This approach has been extended to de Sitter (dS) space to explore the unification of quantum mechanics and general relativity.
5. Dynamic Time Modelling
- Overview: A novel approach to integrating quantum mechanics and general relativity by treating time as a dynamic dimension that behaves differently for different phenomena.
- Key Concept: This approach models time as the plus one (+1) dimension relative to the dimensions through which a given phenomenon propagates and interacts, aiming to integrate mathematical tools from both quantum mechanics and general relativity.
While these theories have made significant strides in unifying quantum mechanics and general relativity, CND theory offers a unique perspective by leveraging numerical value and calculations to create a cohesive framework. This innovative approach has the potential to bridge the gap between these fundamental theories and provide new insights into the nature of reality.
https://researchoutreach.org/articles/unifying-quantum-mechanics-einstein-general-relativity/?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054
https://researchoutreach.org/articles/unifying-quantum-mechanics-einstein-general-relativity/
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5114628&citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5114628
https://www.andrewleeward.com/media/pdf/unification-of-general-relativity-and-quantum-mechanics-v5.pdf?citationMarker=43dcd9a7-70db-4a1f-b0ae-981daa162054
"CND Theory has the potential to create a more cohesive framework that bridges the gap between general relativity and quantum theory" table of contents
- CND Theory has the potential to create a more cohesive framework that bridges the gap between general relativity and quantum theory
- Integrating General Relativity and Quantum Theory
- Numerical Value and Calculation as the Underlying Principle
- Numerical Value and Calculation as the Underlying Principle
- Alignment of Theory: Universe Creation Calculation
